The Researcher’s Impact on Startup Innovation
The Researcher’s Impact on Startup Innovation https://theraise.eu/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/Adriana-Featured-1024x576.jpg 1024 576 RAISE fosters startup growth and scale-up within and across Europe https://theraise.eu/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/Adriana-Featured-1024x576.jpgRAISE organised four events, bringing together researchers and members of the startup ecosystem. These events facilitated matchmaking services, connecting research talent and mentors with startups, scale-ups, startup accelerators, and investors. The pilot actions encouraged scale-ups to showcase their concepts, creating opportunities for impactful ventures and global market matchmaking.
The first event was held on November 3, 2023 on “The Researcher’s Impact on Startup Innovation,” and explored and highlighted the significant influence of researchers in driving innovation within startup ecosystems. The session aimed to provide insights, strategies, and examples showcasing how researchers contribute to pushing the boundaries of knowledge and innovation in the startup landscape with key tactics, recommendations, and real-world examples.
1. Valuable skills researchers possess and their potential impact on the startup ecosystem
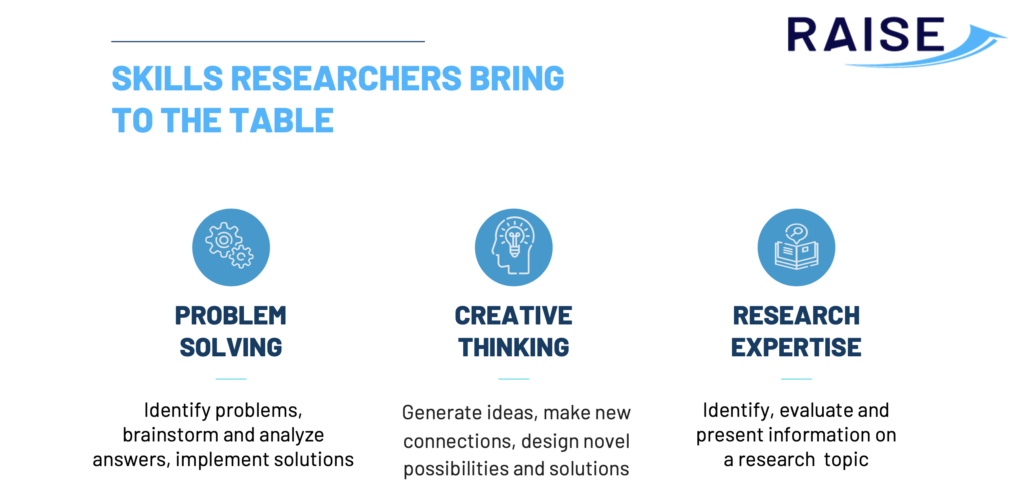
In the dynamic landscape of startups, the collaboration between researchers and entrepreneurs brings a unique set of skills to the table. From problem-solving prowess to creative thinking, researchers contribute significantly to the success and innovation of startups. These are the valuable skills researchers possess and how they can make a substantial impact on the startup ecosystem:
Problem-Solving Expertise
Researchers are adept at identifying problems and developing effective solutions. Their ability to analyse complex issues and generate innovative ideas makes them invaluable assets in the fast-paced startup environment. In startups, where challenges often arise at an accelerated pace, the problem-solving skills of researchers become a critical factor in overcoming obstacles and driving progress.
Creative Thinking
Creative thinking is a shared trait between researchers and startup enthusiasts. Both groups thrive on generating novel ideas, making connections, and exploring new possibilities. Researchers, drawing on their research background, bring a wealth of knowledge and creativity to the startup space. This is particularly crucial in an environment where adaptability and out-of-the-box thinking can make the difference between success and failure.
Research Expertise
While it might seem obvious, the research expertise of individuals is a potent tool that extends far beyond academia. Researchers, trained in specific fields, can apply their knowledge to address challenges in startups. This expertise becomes particularly relevant when communicating with policymakers, as startups navigate the complex landscape of regulations and policy considerations. Researchers, with their deep understanding of scientific principles, become instrumental in communicating with policymakers. This skill is not only crucial in the policy world but also applicable in startups, where regulatory compliance is essential for sustainable growth. The ability to delve deep into a subject and extract valuable insights is a transferable skill. Entrepreneurs can tap into this expertise for informed decision-making and problem-solving.
2. Bridging the Gap: How Researchers Propel Innovation from Lab to Startup
In the ever-evolving landscape of research and innovation, the journey from laboratory discovery to real-world application is a critical process. Researchers play a pivotal role in pushing the boundaries of knowledge and translating their findings into impactful innovations. This content piece delves into the parallels between the research process and the startup world, exploring how researchers can contribute to the thriving ecosystem of innovation.
Creativity in Research and Startups
The research process, characterised by creativity and systematic exploration, shares common ground with the chaotic and dynamic nature of startups. Researchers continuously iterate on ideas, conduct experiments, and seek innovative outcomes. However, transitioning from the structured research environment to the fast-paced world of startups requires a mindset shift to navigate the unpredictability and embrace the chaos inherent in entrepreneurial ventures.
The Role of Tech Transfer Offices
Tech transfer offices act as crucial intermediaries, facilitating the translation of research into marketable innovations. Researchers seeking to commercialise their work can benefit from engaging with these offices. They offer guidance on product development, potential collaborations, and the necessary steps to transform a research project into a startup venture.
Collaborations with Industry
Collaborating with industry partners is essential for researchers looking to bridge the gap between academia and real-world applications. These collaborations provide access to funding, global markets, and industry expertise. Researchers should explore partnerships that align with the goals of their research and have the potential to drive innovation.
Developing Entrepreneurial Skills
Transitioning from academia to entrepreneurship requires researchers to develop entrepreneurial skills. This includes understanding how to navigate the startup ecosystem, pitch ideas, and maintain the momentum of a fledgling company. Recognizing the transferable skills gained through research, such as critical thinking and problem-solving, can empower researchers to thrive in the entrepreneurial space.
Hot Topics and Global Relevance
Researchers should stay attuned to hot topics and societal needs, considering how their discoveries can address pressing issues. Whether it’s environmental challenges, health innovations, or other critical areas, aligning research with global relevance enhances the potential for impactful innovations. Understanding the ever-changing landscape of societal needs informs researchers on where their contributions can make a substantial difference.
Real-World Impact
Practical implications of research findings are integral to the translation of knowledge into real-world impact. Researchers must consider the broader implications of their work, similar to the policy space. Practical considerations include funding, stakeholders, and the potential positive or negative impacts on various sectors.
Clinical Trials and Health Innovations
In the current context, health innovations, especially in the realm of clinical trials, hold significant promise. Researchers should explore avenues where their discoveries can contribute to advancements in healthcare. The creation of new agencies and increased focus on health-related initiatives provide ample opportunities for researchers to turn their ideas into innovative companies.
Bridging the gap between research and startups requires researchers to embrace the challenges and opportunities that come with translating knowledge into innovation. Tech transfer offices, industry collaborations, and a focus on societal needs play crucial roles in this transformative process. As researchers embark on this journey, they contribute not only to the advancement of knowledge but also to the creation of impactful solutions that shape the future.
3. Transforming Research into Societal Solutions
The journey from research laboratories to real-world applications is a critical process that drives innovation and benefits society at large. This content piece explores how research translates into practical solutions with a focus on four key points. Drawing examples from the Science Coalition’s report on sparking economic growth, we delve into the societal impact of research-driven startups.

Diverse Funding Sources and Support
The translation of research into practical solutions often depends on the topic, the spaces involved, and the stakeholders interested in supporting it. Federal funding, whether from agencies or philanthropic sources, plays a crucial role. The Science Coalition emphasizes the link between federal funding, job creation, and economic growth. This comprehensive approach goes beyond creating startups, highlighting the broader societal benefits.
- Example: Ventilators and Respirators – Instruments, a California-based startup, improved respirators for COVID-19 patients, showcasing how research-backed innovations can address urgent societal needs.
Societal Value and Legislative Perspectives
Understanding the societal value of research-driven startups is vital when engaging with legislators. Different legislators may prioritise job creation, economic development, or other factors. Recognizing these intersections helps researchers advocate for funding aligned with legislators’ interests.
- Example: Autism Education – Autism Navigator in Florida focuses on education, developing tools to teach families about autism, emphasising the societal impact of startups beyond medical solutions.
Environmental and Climate Innovations
The ever-popular topics of climate and environment provide fertile ground for research-driven startups. Innovations in environmental solutions, such as tools for groundwater treatment, showcase the potential far-reaching implications for societal benefit.
- Example: Groundwater Treatment – Airlift Environmental, a Nebraska-based startup, develops a pump for treating contaminated groundwater, addressing critical environmental challenges.
Entrepreneurial Mindset and Skill Development
Transitioning from research to entrepreneurship requires the development of an entrepreneurial mindset. Researchers must cultivate skills necessary for startup success, including networking, pitching ideas, and navigating the dynamic startup ecosystem.
- Example: Education and Support – Various programs and initiatives, such as those offered by FAS (Faculty of Arts and Sciences), contribute to skill development and mindset transformation, enabling researchers to thrive in entrepreneurial roles.
Research-driven startups are catalysts for societal change
Research-driven startups are catalysts for societal change, offering practical solutions to pressing issues. By diversifying funding sources, understanding legislative perspectives, addressing environmental challenges, and fostering an entrepreneurial mindset, researchers can contribute to the translation of knowledge into impactful innovations. These examples showcase the wide-ranging societal benefits that emerge when research transforms into tangible solutions, emphasising the importance of continued support for research-driven entrepreneurship.
4. Bridging the Gap: Nurturing Entrepreneurial Roles for Research Impact

As researchers navigate the intricate landscape of turning research into impactful solutions, the development of an entrepreneurial mindset becomes crucial. In this context piece, we explore the entrepreneurial process, emphasising its iterative nature, the importance of thorough research, and the parallel skills required for both research and entrepreneurship.
Iterative Nature of Entrepreneurship
Entrepreneurship shares common ground with research in its iterative nature. While both involve problem-solving, entrepreneurs operate in an environment with less certainty, constantly seeking opportunities and building their own reputation. The emphasis on profits and the need to navigate a dynamic landscape set entrepreneurship apart, requiring a unique skill set.
- Example: Venturing into Startups – Startups often embody the iterative nature of entrepreneurship. A company like Instruments, based in California, iteratively improved respirators for COVID-19 patients, showcasing the adaptability and problem-solving skills essential for entrepreneurial success.
Thorough Research as a Foundation
Research is not only a prerequisite for academic success but is also fundamental to entrepreneurial endeavours. Entrepreneurs must conduct extensive research before venturing into the market, ensuring their ideas are novel, valuable, and address existing gaps. Research becomes the bedrock upon which entrepreneurs build their innovative solutions.
- Example: Educational Tools for Autism – Autism Navigator in Florida exemplifies the importance of thorough research. By developing tools to educate families about autism, they not only addressed a societal need but also conducted research to ensure the effectiveness of their educational approach.
Entrepreneurial Identity and Skill Development
Cultivating an entrepreneurial identity involves understanding the motivations behind venturing into entrepreneurship. The journey parallels the scientific identity, as both require individuals to continuously innovate and build projects. Working in entrepreneurial roles, whether as a CEO or part of a startup, contributes to skill development that is essential for entrepreneurial success.
- Example: Journal of Science Policy and Governance – Serving as the CEO for the Journal of Science Policy and Governance provides individuals with a unique entrepreneurial experience. The role involves leveraging published work through conferences, panels, and media engagement, fostering skills in communication, networking, and impact assessment.
The journey from research to impactful solutions requires researchers to embrace an entrepreneurial mindset. Whether through submitting policy memos, engaging with legislators, or leading roles in research-driven startups, individuals can bridge the gap between research findings and societal impact. By understanding the iterative nature of entrepreneurship, conducting thorough research, and developing an entrepreneurial identity, researchers can contribute to transformative solutions that benefit society.
5. Biotech Startups Transforming Research into Solutions

Biotech startups are at the forefront of leveraging groundbreaking research to bring about transformative solutions in various fields. In this piece, we delve into case studies highlighting how these startups are revolutionising neurology, tissue regeneration, biosupply therapies, bioprinting, and precision agriculture.
Neurology: NotLabs – Precision Medicine Revolution
Innovation: NotLabs has pioneered precision medicine for brain disorders by developing remote-controlled micro-robots. These micro-robots offer a revolutionary approach to diagnosing and treating brain disorders, showcasing the power of precision medicine in the neurology space.
Impact: The ability to remotely navigate micro-robots introduces a new dimension to brain disorder treatment, promising more precise and effective interventions.
Tissue Regeneration: Biosupply Therapies
Innovation: Biosupply Therapies focuses on tissue regeneration and alternative splicing of stem cells to prevent various diseases. Their research extends to regenerating cells in aging individuals, presenting a holistic approach to addressing health challenges associated with aging.
Impact: The company’s innovative therapies offer potential solutions for a myriad of diseases, providing hope for improved health outcomes and enhanced quality of life.
Bioprinting: Advancements in 3D-Printed Human Tissues
Innovation: Bioprinting companies, with a standout example, are actively creating human tissues for medical research and therapy applications. The technology involves 3D printing of organs, offering possibilities for revolutionary advancements in the field of healthcare.
Impact: Bioprinting holds the potential to transform the field of organ transplantation and medical research, providing researchers and clinicians with unprecedented tools to understand and treat diseases.
Precision Agriculture: Climate Corporation – Data-Driven Farming
Innovation: Climate Corporation harnesses data analytics to provide farmers with valuable insights for crop yield improvement. Their precision agriculture approach involves analyzing weather patterns to enable data-driven decision-making for farmers.
Impact: By optimising crop management through data analysis, Climate Corporation contributes to sustainable agriculture, impacting everything from food production to the overall agricultural workforce.
These case studies exemplify the potential of biotech startups in translating research into impactful solutions. From precision medicine in neurology to innovative therapies for tissue regeneration and 3D-printing human tissues, these startups are reshaping industries and offering novel approaches to longstanding challenges. As research continues to drive innovation, biotech startups play a crucial role in bridging the gap between scientific discoveries and real-world applications.
6. Fostering Innovation: The Crucial Link Between Researchers and Startups

We explored the dynamics of fostering innovation through collaborations between researchers and startups. Adriana’s insights shed light on the vital role universities play in providing knowledge, talent, and resources that can be leveraged by startups. Let’s delve into the five key points discussed and explore specific examples.
Universities as Knowledge Hubs
Universities produce valuable knowledge that can be widely leveraged. Collaboration with industry, especially startups, acts as a bridge between theoretical knowledge and practical solutions.
- Example: Research institutions collaborating with biotech startups to advance medical discoveries.
Innovation Funding
Adequate funding is essential for turning research into impactful innovations. Universities can provide facilities and infrastructure, while industry collaboration brings market insights.
- Example: Federally funded programs and initiatives, such as those supporting biotech startups in sparking economic growth.
Talent Development and Experiential Learning
Universities are key drivers of talent development. Experiential learning, mentorship, internships, and support for real-world skills are crucial for preparing students for the industry.
- Example: Programs facilitating internships and co-ops to expose students to industry settings and enhance their understanding of practical applications.
Addressing Important Challenges
Collaboration between researchers and startups can address significant challenges, from agriculture to healthcare. Bridging the gap between academia and industry is crucial for developing impactful solutions.
- Example: Research institutions and startups working together to address challenges like climate change, autism, and sustainable agriculture.
Networking and Translational Connection
Effective networking between researchers, investors, and policymakers is essential. Facilitating transnational connections can bridge the gap between scientific discoveries and real-world applications.
- Example: Researchers engaging with investors and policymakers to facilitate the commercialization of research findings.
7. Q&A session
The Q&A session following Adriana’s presentation provided a platform for probing questions about effectively leveraging research and expertise from academic institutions for startup growth. Here’s a breakdown of the questions and detailed responses.
Question 1: How can startups effectively leverage the research and expertise of academic institutions?
Adriana emphasised the significance of considering commercialization, pointing out areas like drug development and gene therapies, encouraging startups to explore innovative spaces. Funders and legislators play crucial roles; hence, engaging with them becomes vital. We can take a look into drug testing as an example, stating that universities might have limited platforms, and startups could provide tools and platforms to continue the work.
Question 2: How do researchers connect with investors and facilitate translational connections?
Adriana suggested thinking of the big picture and identifying areas where change can happen. Engaging with funders, legislators, and, most importantly, connecting with investors are key steps. She acknowledged the challenge scientists face, primarily being accustomed to lab work. Adriana urged researchers to look beyond, considering policy involvement or contacting their tech transfer office as a small first step.
Question 3: Parallel Perspectives in Europe – Drawing a Parallel Between American and European Startups
Drawing a comparison between American and European startups is valuable. She highlighted the need to explore the conditions under which startups thrive in different regions. This perspective promises to bring valuable insights into the unique challenges and opportunities each region presents.
The Q&A session offered profound insights into the complexities of bridging the gap between academia and startups. Adriana’s responses underscored the importance of strategic networking, engaging with stakeholders, and adopting a holistic approach to innovation. The suggestion to explore regional variations in startup landscapes promises to enrich the ongoing discussion. The intersection of research and entrepreneurship appears as a dynamic space that demands collaboration, adaptability, and an understanding of diverse ecosystems.
8. How has the mentorship program conducted by RAISE demonstrated its impact?
The RAISE session effectively addressed the key goal of bridging researchers and startups. By providing insights and examples, attendees gained knowledge on how universities and startups can collaboratively drive innovation. RAISE further facilitated a deeper understanding of practical steps for effective collaboration, emphasising the importance of strategic networking and engaging with stakeholders. The dynamic interplay between research and entrepreneurship was highlighted as a transformative space demanding collaboration, adaptability, and a nuanced understanding of diverse ecosystems. Collaboration between researchers and startups can address significant challenges. Bridging the gap between academia and industry is crucial for developing impactful solutions.
Key Takeaways
1. Universities as Knowledge Hubs: Universities are knowledge hubs producing valuable insights. Collaboration with startups acts as a bridge between theoretical knowledge and practical solutions.
2. Innovation Funding: Adequate funding is crucial for translating research into impactful innovations. Universities can provide facilities, while industry collaboration brings market insights.
3. Talent Development and Experiential Learning: Universities are key drivers of talent development. Experiential learning, mentorship, internships, and support for real-world skills are crucial for preparing young entrepreneurs for the industry.
4. Talent Development and Experiential Learning: Effective networking between researchers, startups investors, and policymakers is essential. Facilitating translational connections can bridge the gap between scientific discoveries and real-world applications.
Overall, the session set the stage for a continued work on fostering innovation and impactful collaborations between researchers and startups.
About the Speaker and Mentor: Adriana Bankston
Adriana Bankston is a former bench scientist turned science policy expert, with a wealth of experience in research and academic policy changes within university settings. Her career was dedicated to showcasing research discoveries on a broader scale. Notably, Adriana also led a non-profit organisation and held various entrepreneurial roles, connecting with professionals worldwide.

Adriana’s role as a senior fellow in science policy with the Federation of American Scientists showcased her expertise in policy entrepreneurship. Her work at this non-profit mirrored the dynamic nature of a startup, making her well-equipped to discuss the convergence of science and policy.
Based in Washington, DC, USA, Adriana was ideally positioned to offer valuable insights into research-powered innovation, real-world impact, and the art of building strategic partnerships and talent scouting. Her diverse background and passion for research made her a dynamic speaker for discussions surrounding innovation, collaboration, and talent development.
To learn more about Adriana:
- Website: adrianabankston.com
- Biography: FAS – Adriana Bankston


